The database management system can be divided into five major components, they are:
When we run Oracle or MySQL on our personal computer, then our computer's Hard Disk, our Keyboard using which we type in all the commands, our computer's RAM, ROM all become a part of the DBMS hardware.
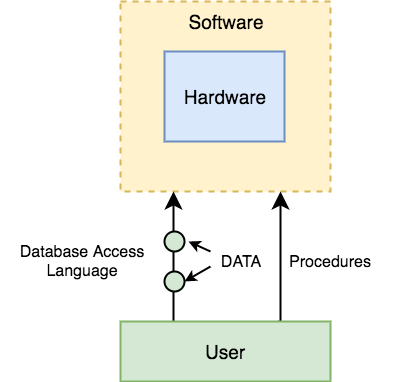
The DBMS software is capable of understanding the Database Access Language and intrepret it into actual database commands to execute them on the DB.
In a typical Database, the user saved Data is present and meta data is stored.
Metadata is data about the data. This is information stored by the DBMS to better understand the data stored in it.
For example: When I store my Name in a database, the DBMS will store when the name was stored in the database, what is the size of the name, is it stored as related data to some other data, or is it independent, all this information is metadata.
A user can write commands in the Database Access Language and submit it to the DBMS for execution, which is then translated and executed by the DBMS.
User can create new databases, tables, insert data, fetch stored data, update data and delete the data using the access language.
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures
- Database Access Language

DBMS Components: Hardware
When we say Hardware, we mean computer, hard disks, I/O channels for data, and any other physical component involved before any data is successfully stored into the memory.When we run Oracle or MySQL on our personal computer, then our computer's Hard Disk, our Keyboard using which we type in all the commands, our computer's RAM, ROM all become a part of the DBMS hardware.
DBMS Components: Software
This is the main component, as this is the program which controls everything. The DBMS software is more like a wrapper around the physical database, which provides us with an easy-to-use interface to store, access and update data.The DBMS software is capable of understanding the Database Access Language and intrepret it into actual database commands to execute them on the DB.
DBMS Components: Data
Data is that resource, for which DBMS was designed. The motive behind the creation of DBMS was to store and utilise data.In a typical Database, the user saved Data is present and meta data is stored.
Metadata is data about the data. This is information stored by the DBMS to better understand the data stored in it.
For example: When I store my Name in a database, the DBMS will store when the name was stored in the database, what is the size of the name, is it stored as related data to some other data, or is it independent, all this information is metadata.
DBMS Components: Procedures
Procedures refer to general instructions to use a database management system. This includes procedures to setup and install a DBMS, To login and logout of DBMS software, to manage databases, to take backups, generating reports etc.DBMS Components: Database Access Language
Database Access Language is a simple language designed to write commands to access, insert, update and delete data stored in any database.A user can write commands in the Database Access Language and submit it to the DBMS for execution, which is then translated and executed by the DBMS.
User can create new databases, tables, insert data, fetch stored data, update data and delete the data using the access language.
Users
- Database Administrators: Database Administrator or DBA is the one who manages the complete database management system. DBA takes care of the security of the DBMS, it's availability, managing the license keys, managing user accounts and access etc.
- Application Programmer or Software Developer: This user group is involved in developing and desiging the parts of DBMS.
- End User: These days all the modern applications, web or mobile, store user data. How do you think they do it? Yes, applications are programmed in such a way that they collect user data and store the data on DBMS systems running on their server. End users are the one who store, retrieve, update and delete data.
Excellent post. You have shared some wonderful tips. I completely agree with you that it is important for any blogger to help their visitors. Once your visitors find value in your content, they will come back for more What is the DBMS and it's uses
ReplyDelete